Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 NCERT Textbook Questions Solved
1. Choose the right answers of the followings from the given options:
Question 1.(i)
Which one of the following is India’s rank in terms of Human Development Index among the countries of the world in 2011?
(a) 126
(b) 134
(c) 128
(d) 129
Answer:
(b) 134
Question 1.(ii)
Which one of the following states of India has the highest rank in the Human Development Index?
(a). Jamil Nadu
(b) Punjab
(c) Kerala
(d) Haryana
Answer:
(c) Kerala
Question 1.(iii)
Which one of the following states of India has the lowest female literacy?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Jharkhand
(d) Bihar
Answer:
(d) Bihar
Question 1.(iv)
Which one of the following states of India has the lowest female child sex ratio 0-6 years?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Haryana
(c) Punjab
(d) Himachal Pradesh
Answer:
(b) Haryana
Question 1.(v)
Which one of the following Union Territories of India has the highest literacy rate?
(a) Lakshadweep
(b) Chandigarh
(c) Daman and Diu
(d) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Answer:
(a) Lakshadweep
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words:
Question 2.(i)
Define Human Development.
Answer:
“Human development is a process of enlarging the range of people’s choices, increasing their opportunities for education, health care, income and empowerment and covering the full range of human choices from a sound physical environment to economic, social and political freedom.”
Question 2.(ii)
Give two reasons for low levels of Human Development in most of the Northern States of India.
Answer:
Kerala with the composite index value of 0.638 is placed at the top rank. There are several socio-political, economic and historical reasons for such a state of affairs. Kerala is able to record the highest value in the HDI largely due to its impressive performance in achieving near hundred per cent literacy (90.92 per cent) in 2001. Apart from the educational attainment, the levels of economic development too play significant impacts on HDI. Lack of awareness and opportunities for education and lack of job opportunities are the reasons for poor development and low HDI ranking in the Northern states of India.
Question 2.(iii)
Give two reasons for declining child sex ratio in India.
Answer:
The main underlying causes is the social attitude of the people which results from the cultural fabric of the country , where there is general preference for male child. People tend to have male children and also there are illegal practices of female infanticide and in modem times pesticides rampant. The states with highest per capita income have lowest child sex ratio because these states have facilities of pre natal sex determination resulting sex selective abortion resulting in low child sex ratio. Also after the birth of female child, the negligence on health care of the female child leads to higher infant mortality rates for female kids resulting in low child sex ratio.
3. Answer the following questions in about 150 words:
Question 3.(i)
Discuss the spatial patterns of female literacy in India in 2001 and bring out the reasons responsible for it.
Answer:
Overall literacy in India is approximately 65.4 per cent (2001) while female literacy is only 54.16 per cent. Total literacy as well as female literacy is higher than the national average in most of the states from south India. There are wide regional disparities in literacy rate across the states of India. There is a state like Bihar which has veiy low (47.53 per cent) literacy and there are states like Kerala and Mizoram which have literacy rates of 90.92 and 88.49 per cent respectively.
Kerala is able to record the highest value in the HDI largely due to its impressive performance in achieving near hundred per cent literacy (90.92 per cent) in 2001. In a different scenario the states like Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Assam and Uttar Pradesh have very low literacy. For example, total literacy rate for Bihar was as low as 60.32 per cent during the same year. States showing higher total literacy rates have less gaps between the male and female literacy rates. For Kerala, it is 6.34 per cent, while it is 26.75 per cent in Bihar and 25.95 per cent in Madhya Pradesh.
Apart from the spatial variations, percentage of literates in the rural areas and among the marginalized sections of our society such as females, scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, agricultural labourers, etc. is very low. It is worth mentioning here that though, there has been improvement in the percentage of literates among the marginalized section yet the gap between the richer and the marginalized sections of the population has increased over the years.
Question 3.(ii)
Which factors have caused spatial variations in the levels of Human Development among the 15 major states in India?
Answer:
India has been placed among the countries with medium human development index. It has human development index of 134. Kerala with the composite index value of 0.638 is placed at the top rank followed by Punjab (0.537), Tamil Nadu (0.531) Maharashtra (0.523) and Haryana (0.509). States like Bihar (0.367), Assam (0.386), Uttar Pradesh (0.388), Madhya Pradesh (0.394) and Odisha (0.404) are at the bottom among the 15 major states in India.
There are several socio-political, economic and historical reasons for such a state of affairs. Kerala is able to record the highest value in the HDI largely due to its impressive performance in achieving near hundred per cent literacy (90.92 per cent) in 2001. States like Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Assam and Uttar Pradesh have very low literacy. States showing higher total literacy rates have less gaps between the male and female literacy rates.
Apart from the educational attainment, the levels of economic development too play significant impacts on HDI. Economically developed states like Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu and Punjab and Haryana have higher value of HDI as compared to states like Assam, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, etc.
Regional distortions and social disparities continue to play an important role in the Indian economy, polity and society. In India, social divisions of caste, religion, sex plays an important role in the access of the particular social group to various life chances, hence alter their standing in the human development index. It is found that states with wider variations in social group like Uttar Pradesh tend to have lower Human development index due to communal tensions, differential resource distribution to people of different social groups.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 NCERT Extra Questions
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the states with lowest & highest percentage -of people below poverty line.
Answer:
As per 2001 data of Planning Commission of India the state with lowest percentage of people below poverty line is Jammu and Kashmir, where Odisha has the highest number of people below poverty line.
Question 2.
Which factors differentiate states with high HDI value from low HDI value?
Answer:
There are several socio-political, economic and historical reasons that differentiate the states with high frbm states with low HDI values.
Question 3.
What do you mean by development?
Answer:
It is freedom which is often associated with modernisation, leisure, comfort and affluence. In the present context, computerisation, industrialisation, efficient transport and communication network, large education system, advanced and modern medical facilities, safety and security of individuals, etc. are considered as the symbols of development.
Question 4.
‘Development is biased’. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Development of a few regions, individuals brought about in a short span of time leads to poverty and malnutrition for many along with large scale ecological degradation. It makes one feel that development is biased. But actual development is one which improves quality of life for one and all.
Question 5.
What components are considered as symbols of development?
Answer:
Computerization, industrialization, efficient transport and communication network, large education system, advanced and modern medical facilities, safety and security of individuals, etc. are considered as the symbols of development.
Question 6.
Explain the meaning of development in context of India.
Answer:
Every individual, community and government measures its performance or levels of development in relation to the availability and access to some of these things. But, this may be partial and one-sided view of development.
Question 7.
Who are the most marginalized group in Indian context?
Answer:
It is a well-established fact that majority of the scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, landless agricultural labourers, poor farmers and slums dwellers, etc. are the most marginalized group in Indian context.
Question 8.
What is special in Human Development Report, 1993?
Answer:
According to the Human Development Report 1993, “progressive democratization and increasing empowerment of people are seen as the minimum conditions for human development”. Moreover, it also mentions that “development must be woven around people, not the people around development”.
Question 9.
On what basis has Planning Commission of India prepared Human Development Report?
Answer:
Using the indicators selected by the UNDP, the Planning Commission of India also prepared the Human Development Report for India. It used states and the Union Territories as the units of analysis. Subsequently, each state government also started preparing the state level Human Development Reports, using districts as the units of analysis.
Question 10.
What is considered the key to human development?
Answer:
Enlarging the range of people’s choices is the most significant aspect of human development. People’s choices may involve a host of other issues, but, living a long and healthy life, to be educated and have access to resources needed for a decent standard of living including political freedom, guaranteed human rights and personal self-respect, etc. are considered key to human development.
Question 11.
“Poverty is a state of deprivation”. Explain.
Answer:
Poverty is a state of deprivation. In absolute terms, it reflects the inability of an individual to satisfy certain basic needs for a sustained, healthy and reasonably productive living. It is a state where a person is deprived of even the most basic needs of life.
Question 12.
Life free from illness and ailment and living a reasonably long lifespan are indicative of a healthy life. Explain.
Answer:
Availability of pre and post-natal health care facilities in order to reduce infant mortality and post delivery deaths among mothers, old age health care, adequate nutrition and safety of individual are some important measures of a healthy and reasonably long life.
Question 13.
‘Development is freedom’. What does this statement signify?
Answer:
‘Development is freedom’. It means freedom from hunger, poverty, servitude, bondage, ignorance, illiteracy and any other forms of domination is the key to human development. Freedom in real sense of the term is possible only with the empowerment and participation of the people in the exercise of their capabilities and choices in the society.
Question 14.
In which states is the literacy rate high?
Answer:
Total literacy as well as female literacy is higher than the national average in most of the states from South India. [Kerala and Mizoram have literacy rates of 90.92 and 88.49% respectively].
Question 15.
Name five countries with the highest HDI ranking.
Answer:
Norway has the highest HDI index in the world with 0.963 followed by Australia with 0.955, Sweden with 0.949, Switzerland with 0.947 and USA with 0.944.
Question 16.
Which five states of India have the lowest rank in HDI?
Answer:
In India, Human Development Index of Bihar is 0.367 followed by Assam with 0.386, Uttar Pradesh with 0.388, Madhya Pradesh with 0.394 and Odisha with 0.404.
Question 17.
Which country has proclaimed ‘Gross National Hapiness’ as the measure of a country’s progress?
Answer:
Bhutan has proclaimed ‘Gross National Hapiness’ as the measure of a country’s progress.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
List the factors which might have caused India’s poor showing/ranking in HDI ranking.
Answer:
India with a population of 1.2 billion is ranked 134th out of 172 countries as per the UNDP HDI report 2011, with a value of 0.547. There are various historical factors which are responsible for India’s poor ranking in HDI like colonialisation, social-cultural factors like Human Right violation, social discrimination on the basis of race, religion, gender and caste, social problems like crime, terrorism and lower level of empowerment among marginal members of society has special significance in this regard.
Question 2.
List three interesting features of India’s literacy as per 2001 census report
Answer:
The three interesting features of India’s literacy as per 2001 census report are:
- Overall literacy in India is approximately 65.4 per cent (2001). While female literacy is 54.16 per cent.
- Total literacy as well as female literacy is higher than the national average in most of the states from south India.
- There are wide regional disparities in literacy rate across the states of India. There is a state like Bihar which has very low (47.53 per cent) literacy and there are states like Kerala and Mizoram which have literacy rates of 90.92 and 88.49 per cent respectively.
Question 3.
Which factors are responsible for the variation in Human Development among the states of India?
Answer:
There are several socio-political, economic and historical reasons for such a state of affairs. Kerala is able to record the highest value in the HDI largely due to its impressive performance in achieving near hundred per cent literacy. States like Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Assam and Uttar Pradesh have very low literacy. States showing higher total literacy rates have less gaps between the male and female literacy rates.
Apart from the educational attainment, the levels of economic development too play significant impacts on HDI. Economically developed states like Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu and Punjab and Haryana have higher value of HDI as compared to
states like Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, etc.
Regional distortions and social disparities play an important role in the Indian economy, polity and society. The Government of India has made concerted efforts to institutionalize the balanced development with its main focus on social distributive justice through planned development.
Question 4.
What are the direct bearings of development on deteriorating human conditions?
Answer:
Developmental activities causes environmental pollution and ecological crises. It leads to air, soil, water and .noise pollution’s and threaten the existence of a society. The poor are subjected to three interrelated processes of declining capabilities; i.e.
- social capabilities – due to displacement and weakening social ties (social capital),
- environmental capabilities – due to pollution and,
- personal capabilities – due to increasing incidence of diseases and accidents.
This, in turn, has adverse effects on their quality of life and human development. So, developmental activities are considered as a main source of social distributive injustice, deterioration in the quality of life, ecological crises and social unrest.
Question 5.
Mention the important measures of a healthy and long life.
Answer:
- Life free from illness and ailment and living a reasonably long lifespan are indicative of a healthy life.
- Availability of pre and post-natal health care facilities in order to reduce infant mortality and post delivery deaths among mothers.
- Old age health care.
- Adequate nutrition.
- Safety of individuals.
Question 6.
Mention the major issues which UNDP considered important in achieving Human development.
Answer:
- People’s participation and their security
- Democratization
- Increasing empowerment of people
- Bringing about peace and human development
- Reduction in the military expenditure, ’ demobilization of armed forces, transition from defence to production of basic goods and services and particularly disarmament and reduction in countries.
- Peace and well-being are major global concerns.
Question 7.
Explain the level of literacy in India.
Answer:
Overall literacy in India is approx. 5.4% while female literacy is 54.16%.
- Total literacy as well as female literacy is higher than the national average in most of the states from South India.
- There are wide regional disparities in literacy rate across the states of India.
- States like Bihar has a very low (47.53%) literacy whereas states like Kerala and Mizoram have literacy rates of 90.92 and 88.49% respectively.
- Percentage of literate in the rural areas and among the marginalized sections of our society such as females, SC’s, ST’s and agricultural labourers is very low.
Question 8.
Explain thoughts of Mahatma Gandhi in context of development.
Answer:
Indian culture and civilization have been very sensitive to the issues of population resource and development for a long time.
- Mahatma Gandhi in recent time advocated for the reinforcement of harmony and balance between the two, that is population resource and development.
- He was quite apprehensive about the on¬going development particularly the way industrialization has institutionalized the loss of morality, spirituality, self¬reliance, non-violence, and mutual cooperation and environment.
- Austerity for individuals, trusteeship of social wealth and non-violence are the key to attain higher goals in the life of an individual as well as that of a nation.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write a report on the Human Development in India from the point of economic, health & social empowerment.
Answer:
It is believed that “Development is freedom” which is often associated with modernization leisure, comfort and affluence. In the present context computerization, industrialization, efficient transport and communication network, large education system, advanced and modern medical facilities, safety and security of individuals, etc. are considered as the symbols of development.
Indicators of Economic Attainments: A rich resource base and access to these resources by all, particularly the poor, downtrodden and the marginalized is the key to productivity, well-being and human development. Gross National Product (GNP) and its per capita availability are taken as measures to assess the resource base/endowment of any country. Prevalence of poverty, illiteracy, deprivation and injustice in social distribution system and regional disparities belie all the economic achievements in India. Developed states like Maharasthra, Punjab, Haryana and Gujarat have high per capita income. The poorer states of U.P., Bihar, Odisha, M.P., Assam have less per capita income. In states like Odisha and Bihar more than 40% population live below poverty line.
Indicators of Healthy Life: A disease free and a relatively long life is indicator of healthy life. Some of the measures of healthy life are availability of pre and post natal healthcare system facilities, old age health care, adequate nutrition and safety of individuals. Over the years the death rate has come down from 25.1 per thousand in 1951 to 8.1 per thousand in 1999. Birth rate has gone down from 40.8 to 26.1 during the same time period. The life expectancy has increased from 37.1 years to 62.3 years for males and 36.2 to 65.3 years for females from 1951 to 1999. India has recorded a declining sex ratio except in the state of Kerala.
Social Empowerment: Freedom in real sense of the term is possible only with the empowerment and participation of the people in the exercise of their capabilities and choices in the society. Access to knowledge about the society and environment are fundamental to freedom. Literacy is the beginning of access to such a world of knowledge and freedom. In India the overall literacy rate is 65.4% (2001) and female literacy is 54.1%, ranging from 47% in Bihar to 91% in Kerala. It has been observed that literacy rate is more in southern states than the national average. Apart from the spatial variation, literacy rate is lower in rural areas and marginalized sections of the society. Though the literacy rate has increased among the marginalized section, yet the gap has increased between them and the rich.
Question 2.
With example show how population, development and environment are inter related?
Answer:
There is a general notion that if development is achieved then it will solve all the social-cultural and environmental problems of the society. Development, along with it has increased regional disparities, social inequality, displacement of people, discrimination, deprivation, abuse of human rights and human values and has led to environmental degradation.
UNDP in its human development report 1993 laid emphasis on progressive democratization and increasing empowerment of people. It recognized the constructive role of civil society in bringing peace and human development for reduction in military expenditure, demobilization of armed forces and transition from defence to production of basic goods and services.
The neo-Malthusian environmentalists believe that proper balance between population and resources is necessary for happy and peaceful social life. Developmental activities have increased the multiple uses of the limited available resources in order to cater to the growing demand, but since resources are unevenly distributed so there is injustice in social distribution. The richer countries have more access while the resources are shrinking in poorer countries, thereby leading to conflict as well as apparent contradiction between population, resource and development.
Indian culture is concerned about the balance and harmony among the elements of nature. According to Gandhiji austerity for individual, trusteeship of social wealth and non- violence are the key to attain higher goals in the life of an individual as well as that of a nation.
Question 3.
“Development is a mix bag of opportunities as well as neglect and deprivation”. Explain.
Answer:
There are a few areas like the metropolitan centers and other developed enclaves that have all the modern facilities available to a small section of its population. At the other extreme of it, there are large rural areas and the slums in the urban areas that do not have basic amenities like potable water, education and health infrastructure available to majority of this population. The situation is more alarming if one looks at the distribution of the development opportunities among different sections of our society.
It is a well established fact that majority of the scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, landless agricultural labourers, poor farmers and slums dwellers, etc. are the most marginalized lot. A large segment of female population is the worst sufferers among all. It is also equally true that the relative as well as absolute conditions of the majority of these marginalized sections have worsened with the development happening over the years. Consequently, vast majority of people are compelled to live under abject poverty and subhuman conditions. There is yet another inter-related aspect of development that has direct bearings on the deteriorating human conditions. It pertains to the environmental pollution leading to ecological crisis.
Question 4.
Describe the level of economic achievements in India.
Answer:
The level of economic achievements in India can be understood from the following:
- Gross National Product (GNP) and per capita availability are taken as measures to access the resource base of any country. GDP was ? 3200 thousand crores and according to per capita income it was ? 20,813.
- Prevalence of poverty, deprivation, malnutrition, illiteracy various types of prejudice and above all social distributive injustices and large scale regional disparities.
- Few developed states like Maharashtra, Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat and Delhi that have per capita income more than ? 4,000 per year and a large number of poorer states like U.P. Bihar, Odisha, M.P., Assam, J&K have recorded per capita income less than ? 2,000.
- The developed states have higher per capita income consumption expenditure as compared to the poorer states.
- These variations are indicative of deep- seated problems of poverty, unemployment and under-employment.
- States like Bihar and Odisha have recorded more than 40 per cent population living below poverty line.
- Employment rate for educated is 25%. Jobless growth and rampant unemploy¬ment are some of the important reasons for higher incidences of poverty in India.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Differentiates
Question 1.
Distinguish between human development and economic development.
Answer:
| Human Development | Economic Development |
| (i) It means the well-being of people in its broad perspective, for example, Social economic and cultural development. | (i) The concept of economic development exclusively focuses on increase in income. |
| (ii) It cannot be achieved without economic growth. | (ii) It depends on development of technology and education. |
| (iii) It should be around people. | (iii) It is achieved through GNP and per capita income. |
| (iv) It helps in raising the level of well-being. | (iv) It can be achieved through skills and knowledge of utilizing resources. |
| (v) People must have opportunities to invest in improvement of health education, training. | (v) It is essential for the improvement of standard of living and well-being. |
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
Question 1.
Do you agree that “development must be woven around people, not the people around development”? Illustrate.
Answer:
Yes, I agree that “development must be woven around people, not the people around development”. For this we need following steps:
- Orientation towards sustainable development.
- Empowerment of people.
- Encouraging democratization.
- Efforts to remove regional imbalances.
- Maximization of expenditure on welfare.
- Building human capabilities in the field of health, education and access to resources.
Question 2.
The prime task before any development activity is to maintain parity between population and resources. Elaborate it in the light of NeoMalthusian theory.
Answer:
It is absolutely right to say that the prime task before any development activity is to maintain parity between population and resources.
- Proper balance between population and resources.’
- To reduce the gap between population and resources.
- Limited resources but increase in demand due to population explosion.
- Over exploitation of the resources by rich and powerful people leads to conflicts and contradictions in the society.
Question 3.
What are the reasons behind male- female literacy gaps?
Answer:
Following are the reasons behind male-female literacy gaps:
- Sexual division of labour: Since ancient times, it is assumed that economic and social activities are part of males and females should stay at home for bearing and rearing up of children. It has developed an attitude that education is not as important for females as it is for males.
- Security: In some regions schools are located at distance and it is not safe to send girls alone to such far off places.
- Marriage System: In India, girls leave their parents’ home after marriage. So they feel that investing in girls education will give as much rewards as investment in the boys’ education. So parents are willing to spend more on the education of their sons.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Map Based Questions
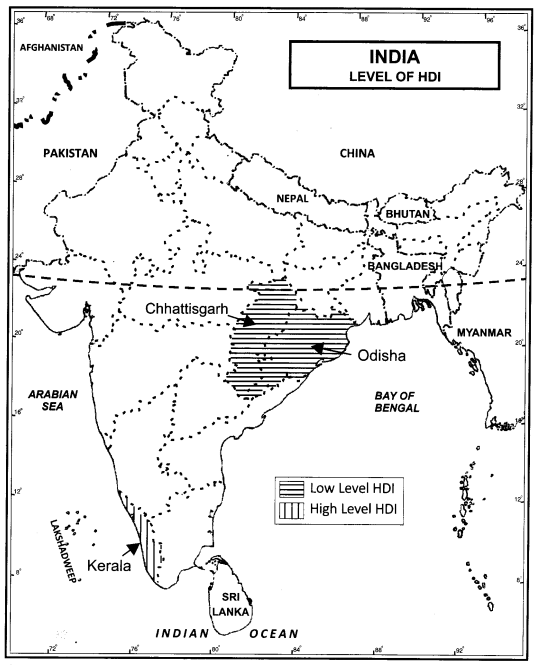
Question 1.
Locate and label the following on the given political map of India with appropriate symbols:
(i) State having low level H.D.I.
(ii) State having high level H.D.I.
Answer:
(i) Chhattisgarh and Odisha
(ii) Kerala
Question 2.
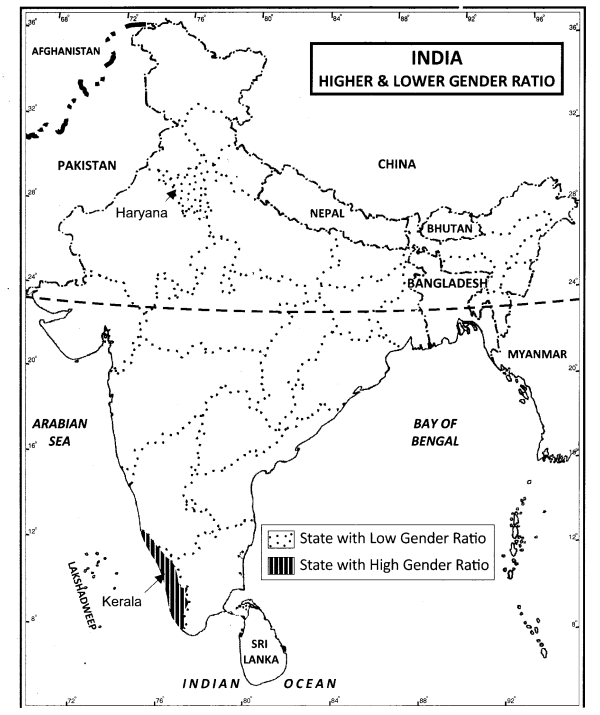
Locate and label the following on the given political map of India with appropriate symbols:
(i) State having low gender ratio.
(ii) State having high gender ratio.
Answer:
(i) Haryana
(ii) Kerala
Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Important Questions
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Which state of India has the lowest literacy rate? Mention its literacy rate also. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Bihar, 47.53 per cent.
Question 2.
Name the two states of India which have less than five per cent of the population below poverty line. (A.I. 2009)
Answer:
Goa and Jammu & Kashmir.
Question 3.
Mention any two key areas of measuring “human development’. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- Health
- Education
- Access to resources.
Question 4.
Which state of India has the lowest female literacy rate? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Rajasthan (52.66%) (2011) state has the lowest female literacy rate in India.
Question 5.
Which state of India has the highest rank in Human Development Index (HDI) value? (CBSE 2012, A.1.2014)
OR
Which state of India has the top rank in the ‘Human Development Index? (Foreign 2010)
Answer:
Kerala ranks the highest value of 0.790 (2007-08).
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
“Development is general and human development in particular is a complex concept used in social science.” Justify this statement with suitable arguments. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
No doubt human development is a complex because for ages it was thought that the development is a substantive concept. Once it is achieved it will address all the social-cultural and environmental ills of the society. Though development has brought improvement in the quality of life but more than one way it has increased regional disparities social inequalities, discrimination, deprivation and displacement of people.
Considering the gravity and sensitivity of the issues involved, the UNDP in its Human Development Report, 1993 tried to amend some of the implicit biases and prejudices. People participation and their security were the major issues in the Human Development Report of 1993 It also emphasized on progressive democratization and increasing empowerment of people as minimum conditions for human development.
The ‘civil societies’ should work to building up opinion for reduction in the military expenditure. In a nuclearised world, peace and well being are major global concerns.

Leave a Reply